Robots able to walk by active or pasive actuator.
Applied in humanoids, exoskeletons, Linkage mechanism and bio-mimetically inspired.
Type of walk
Walk displacement can be reproduced by any number of legs; some other motions can be development by legs like: jump, run, climb, etc.
Linkage mechanism
The linkage bars are arranged as a mechanical leg that can perform planar or composite motions. When one foot (leg) is touching the ground, the others should stand-up & move as fast as possible.

Salamander like robot platform
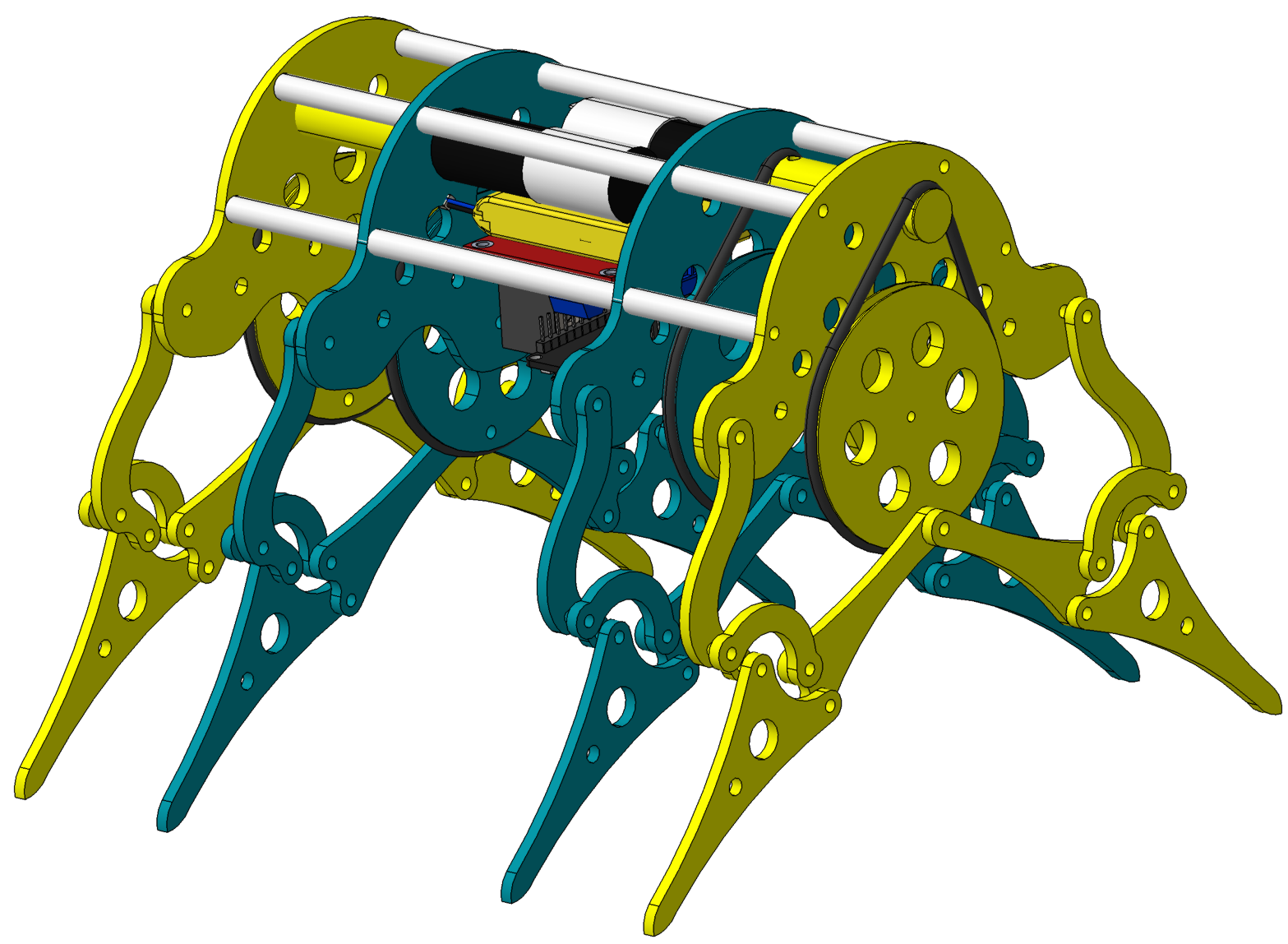
Quadruped robot controlled via IoT.
Salamander robot with 23 servo-actuators inspired from emperor newt.
Colombia - 2023

Humanoid like robot platform
Bipedal Robot controlled via IoT.
Humanoid robot with 5 DOF Legs and 3 DOF Arms.
Colombia - 2022

Mobile wheels-legged Robot
Mobile hybrid platform of quadruple wheel and legs robot.
Platform with 4 active dc motors and 8 servo motors.
Colombia - 2022
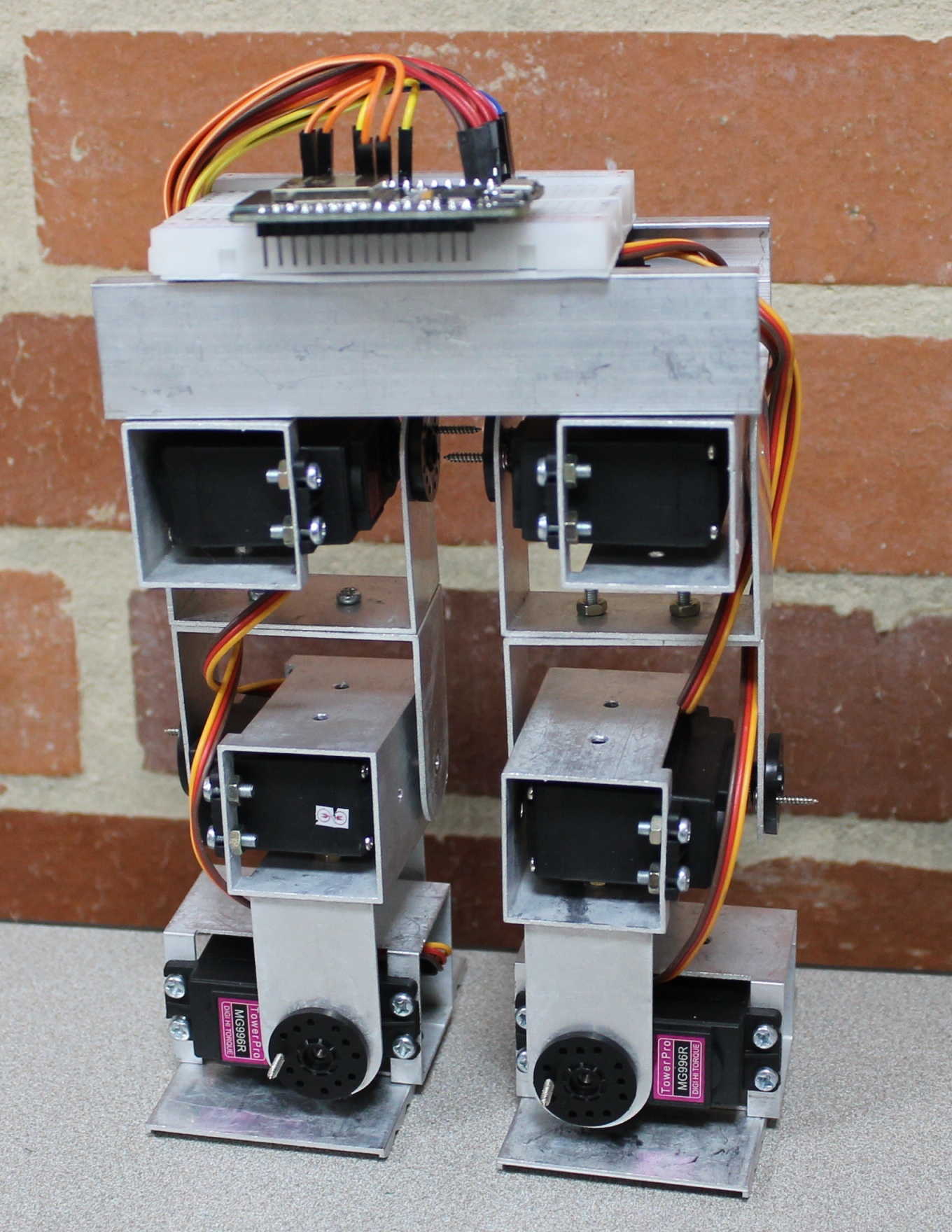
Modular bipedal robot
IoT Walking Robot.
Student project of leg mechanism controlled via IoT.
Colombia - 2023
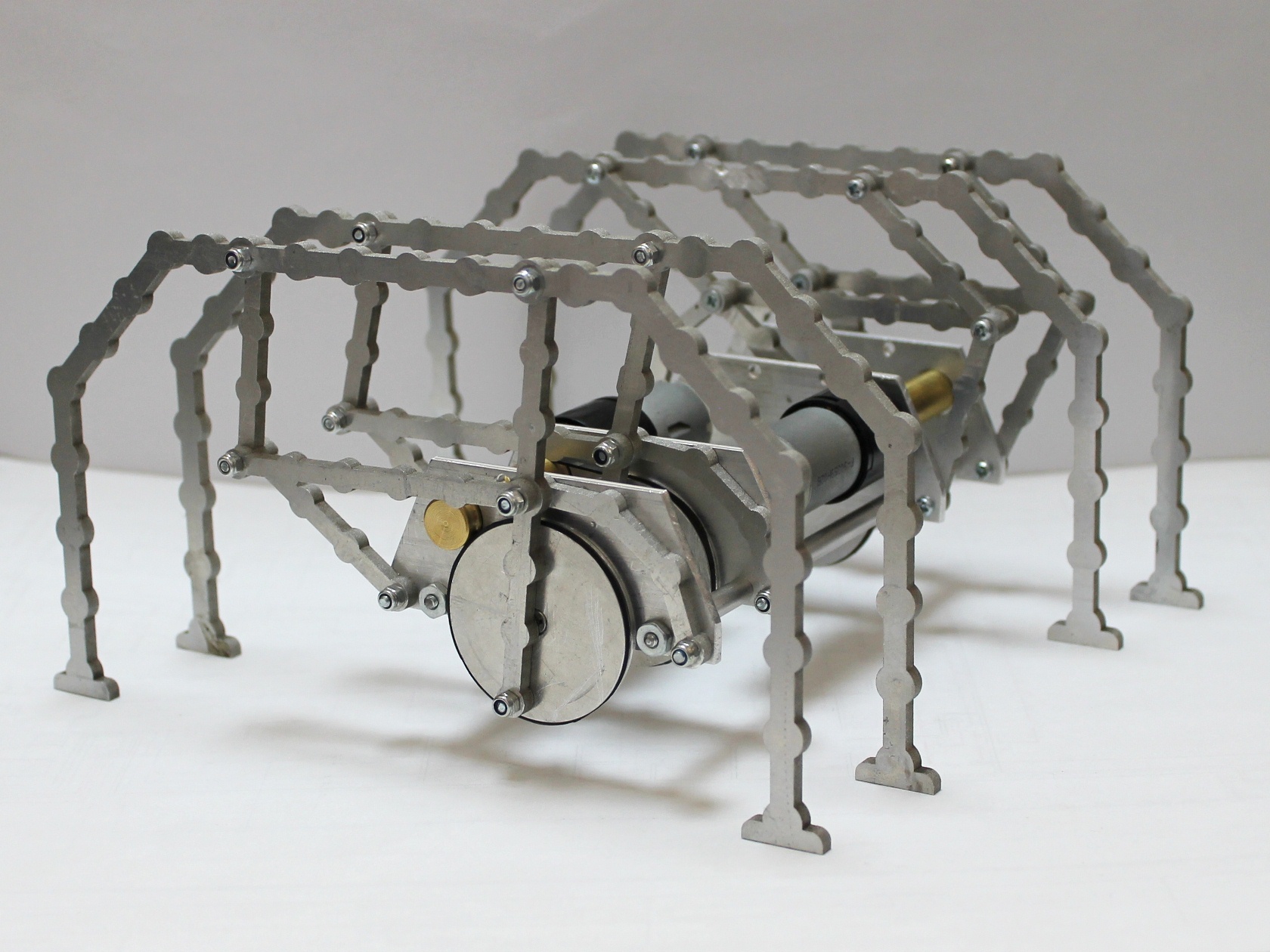
Chebyshev´s linkage mechanism
Linkage mechanism that converts rotational motion to approximate straight-line motion. Invented by Pafnuty Chebyshev in 19th century.
Four-links leg mechanism.
Colombia - 2022
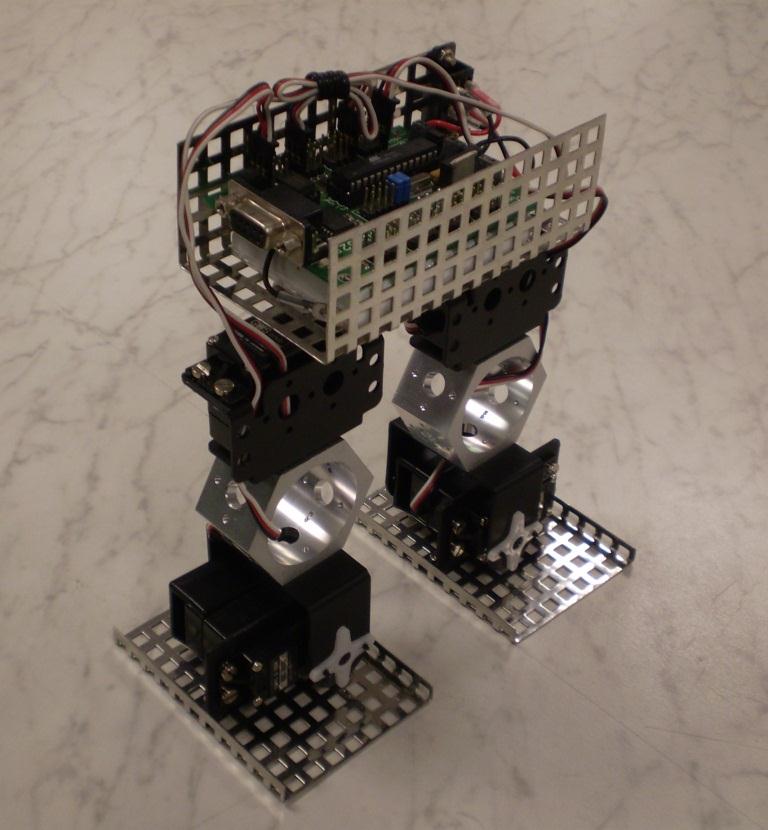
Bipedal robot
Walking with Robots.
Royal Academy of Engineering - London Engineering Project.
England - 2007
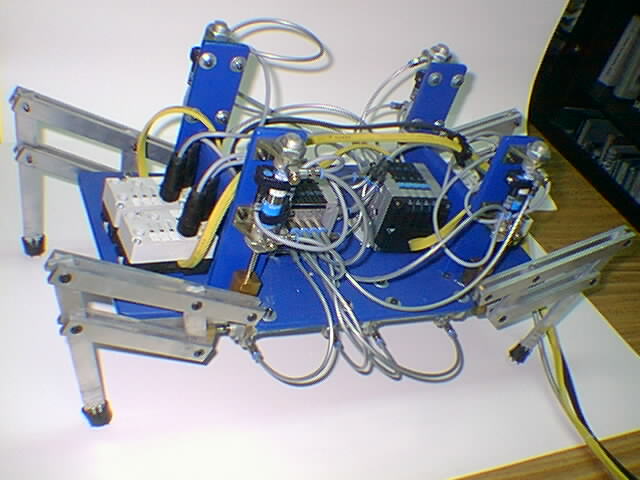
Quadruped Robot
Quadruped walking robot.
Electro-Pneumatics Robot with Quadruped Locomotion Controlled via AS-i Fieldbus.
Colombia - 2000

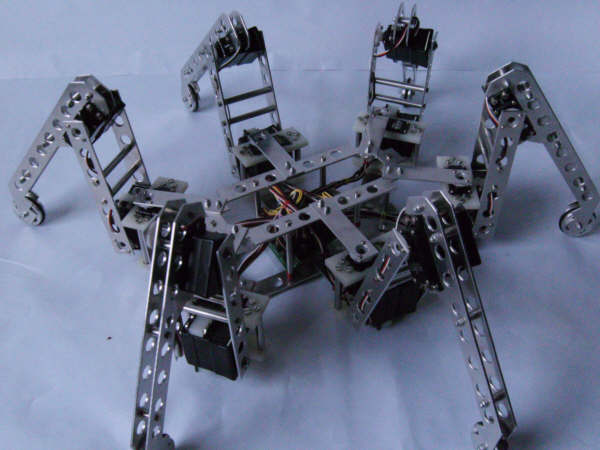
Hexapod Robot
Six Legs robot with 18 DOF.
Bio-mimetically inspired spider like robot.
England, Colombia - 2008

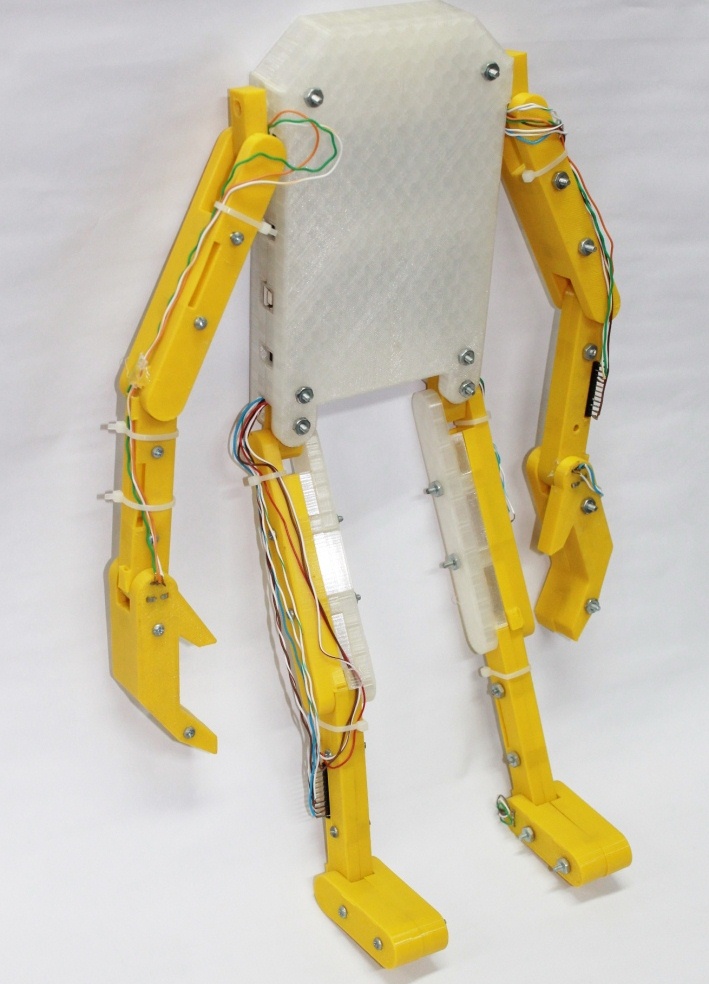
Humanoid Robot
Bipedal Robot controlled via wirelessly.
Humanoid robot with 3 DOF Legs and 4 DOF Arms.
Colombia - 2009
Motion Capture Robot
Humanoid robot for 3D capture animation motion.
Pasive motion robot with 16 DOF.
Colombia - 2013
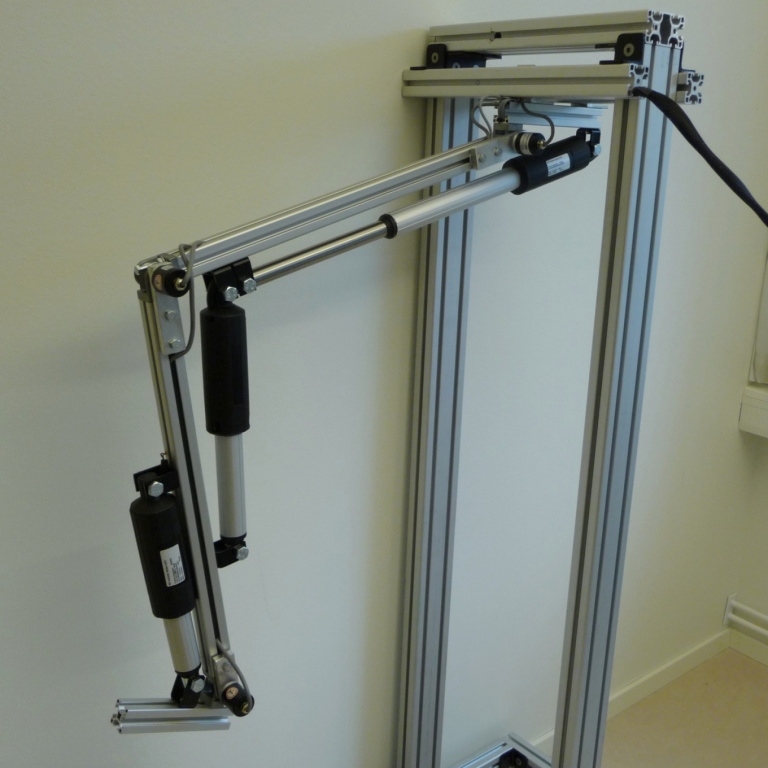

Exoskeleton Robot
Bipedal walking robot.
Exoskeleton Robot for Elderly and Disabled Persons.
Sweden - 2011

Centipede Micro-robot
Walking micro-robot with electromagnetic actuations.
Bio-mimetically inspired centipede like robot.
Korea - 2015

Klann´s linkage mechanism
Planar mechanism designed by Joseph Klann in 1998 to simulate the gait of legged animal.
Six-links leg mechanism.
Colombia - 2021
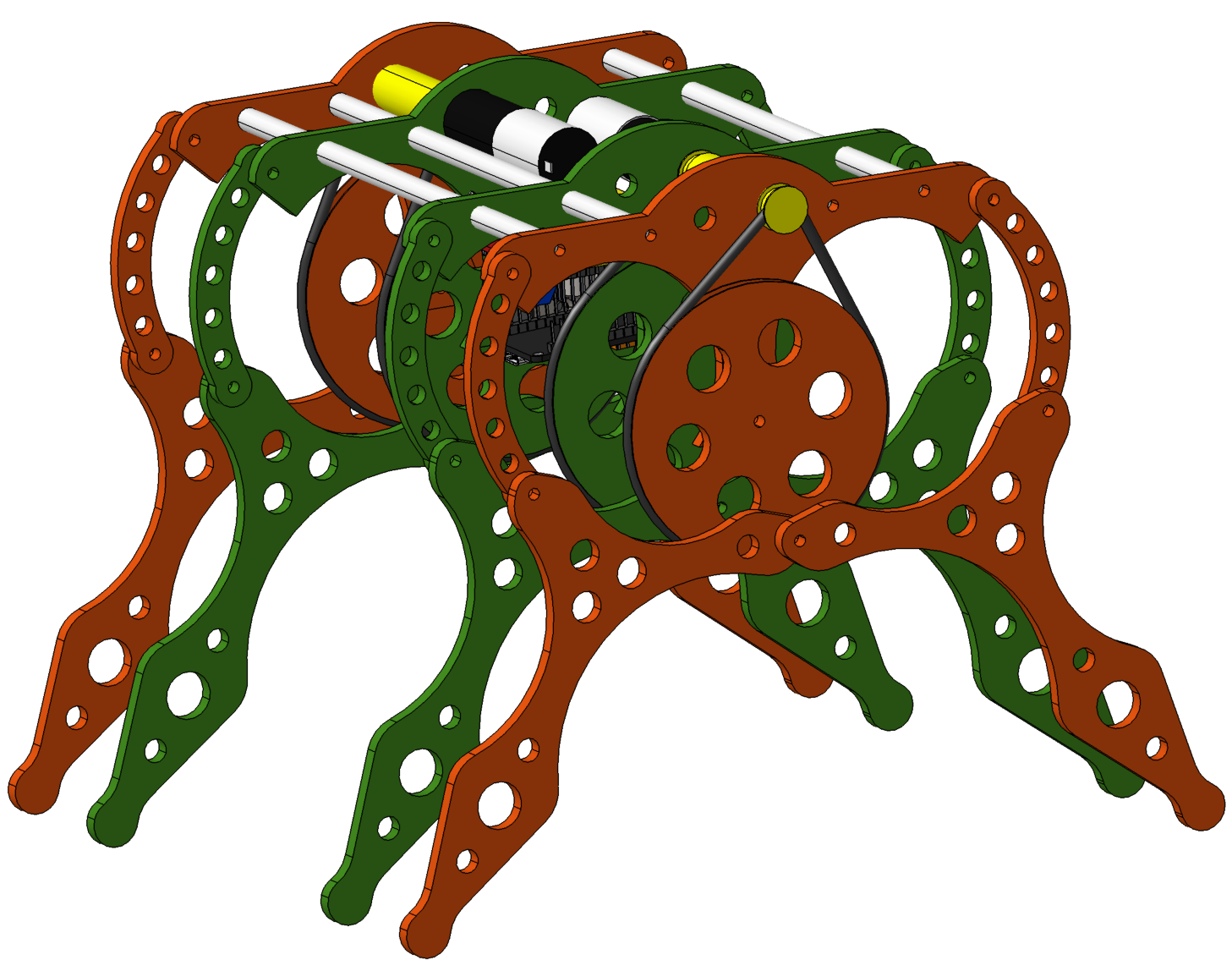
Hrones-Nelson´s linkage mechanism
The mechanism is four links pinned together to form a closed loop. Published by Hrones and Nelson in 1951.
Four-links leg mechanism.
Colombia - 2021
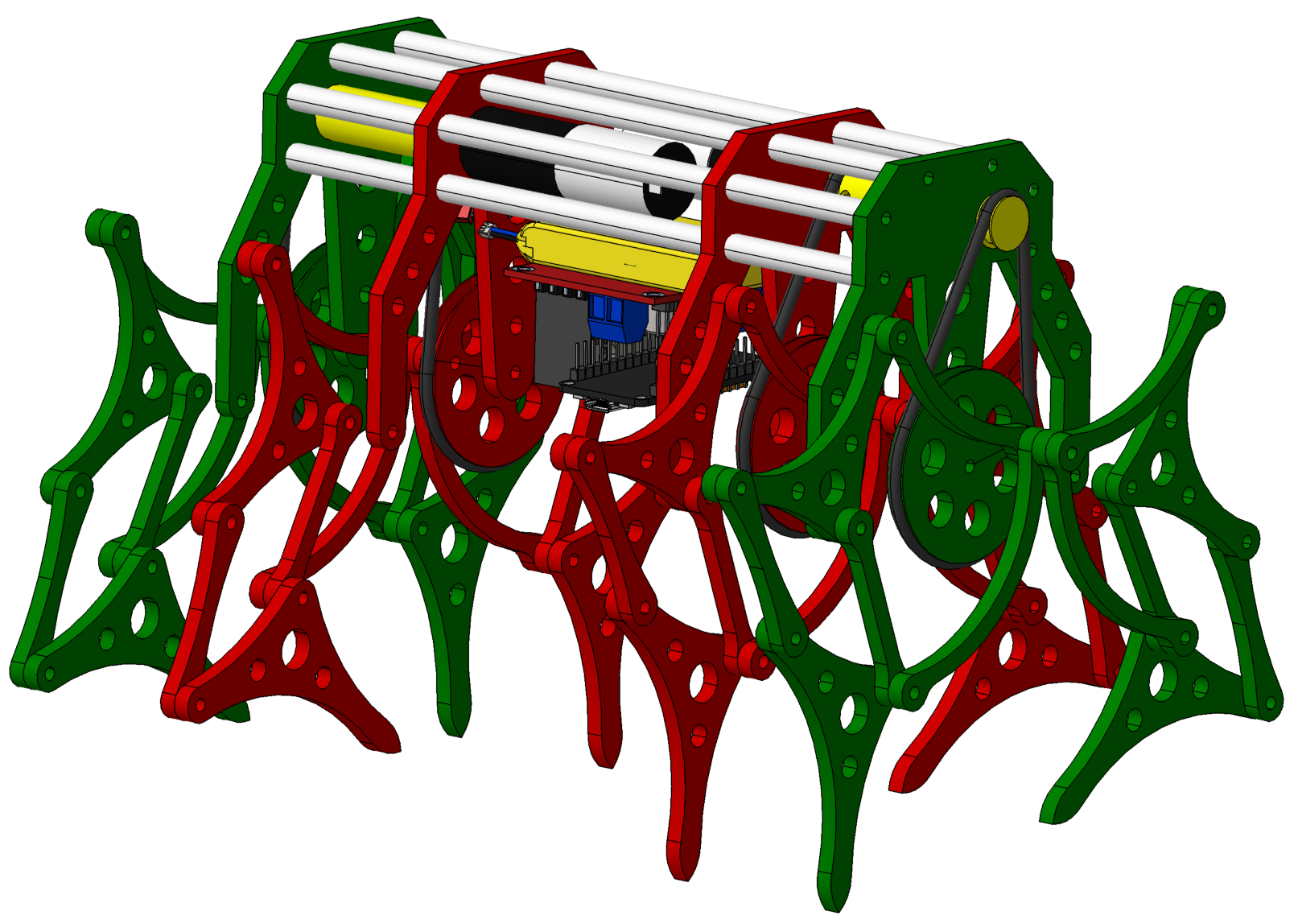
Jansen´s linkage mechanism
Planar leg mechanism designed by Theo Jansen in 1991 to generates a smooth walking motion.
Six-links leg mechanism.
Colombia - 2021
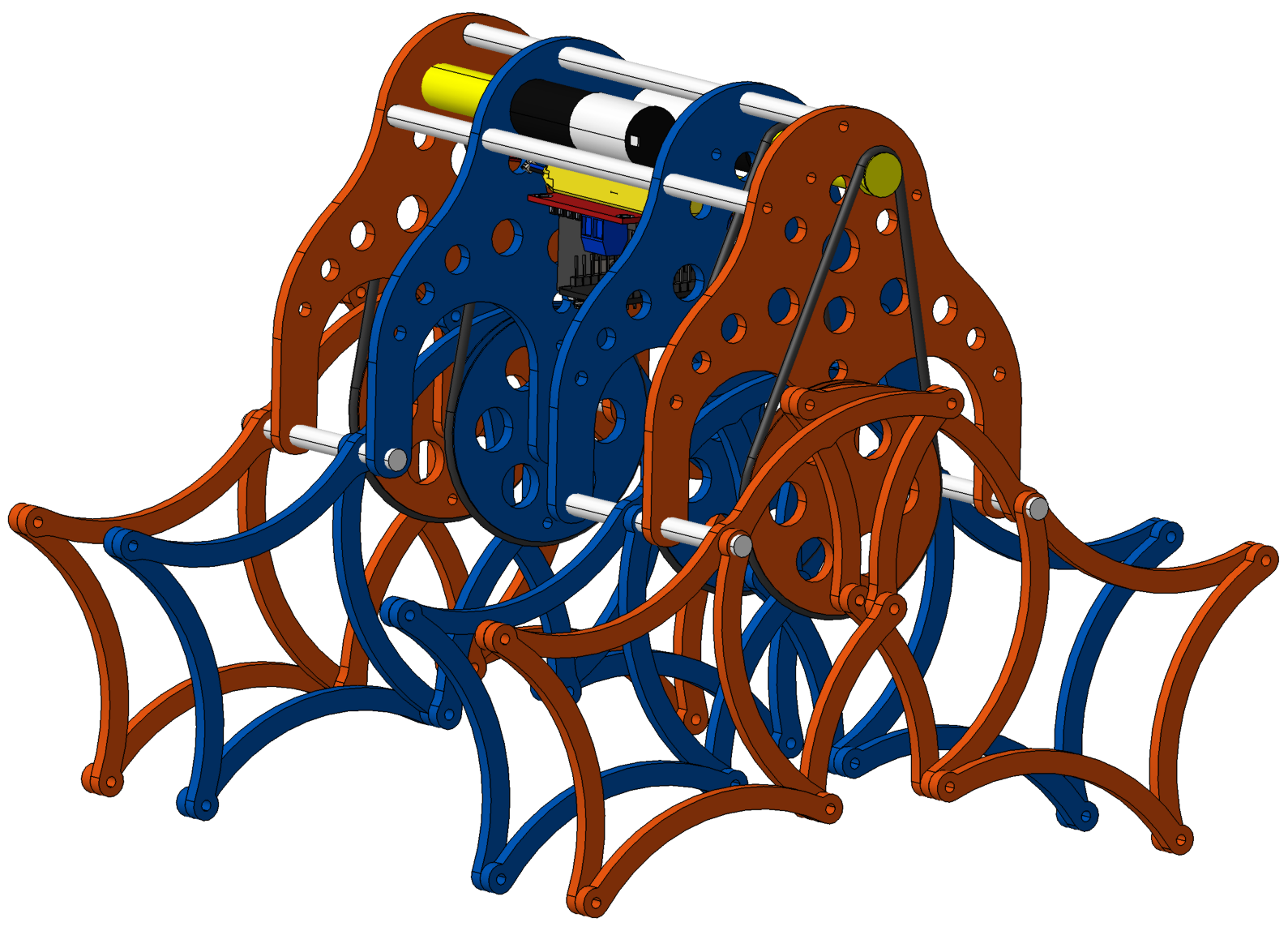
Ghassaei´s linkage mechanism
Designed by Amanda Ghassaei in 2011; her achievement was combination of efficiency, stability, and step height for a large kinetic sculpture.
Eight-links leg mechanism.
Colombia - 2021
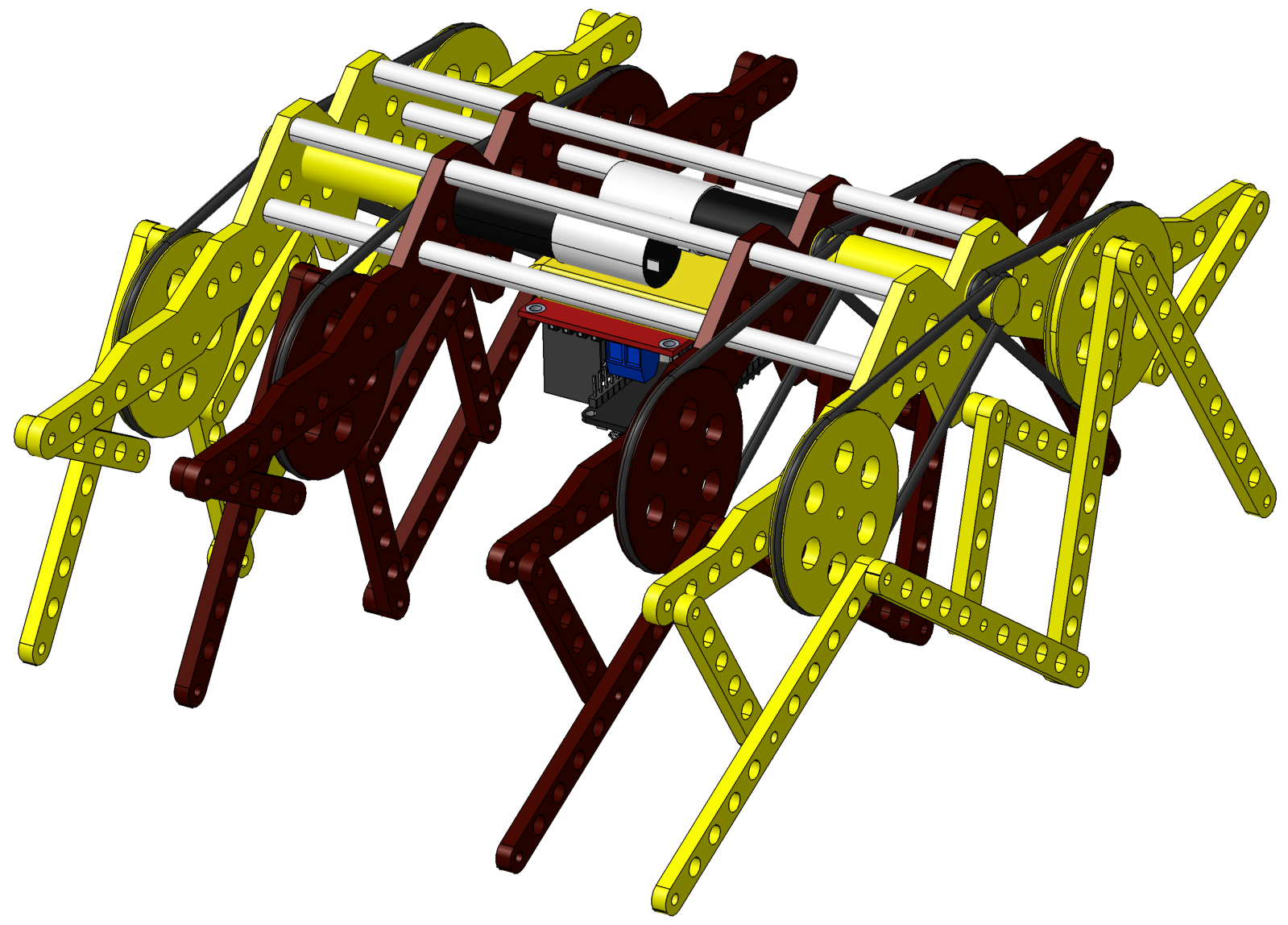
Frey´s linkage mechanism
Extra-simple planar linkage mechanism; designed by Michael Frey in 2016
Four-links leg mechanism.
Colombia - 2021
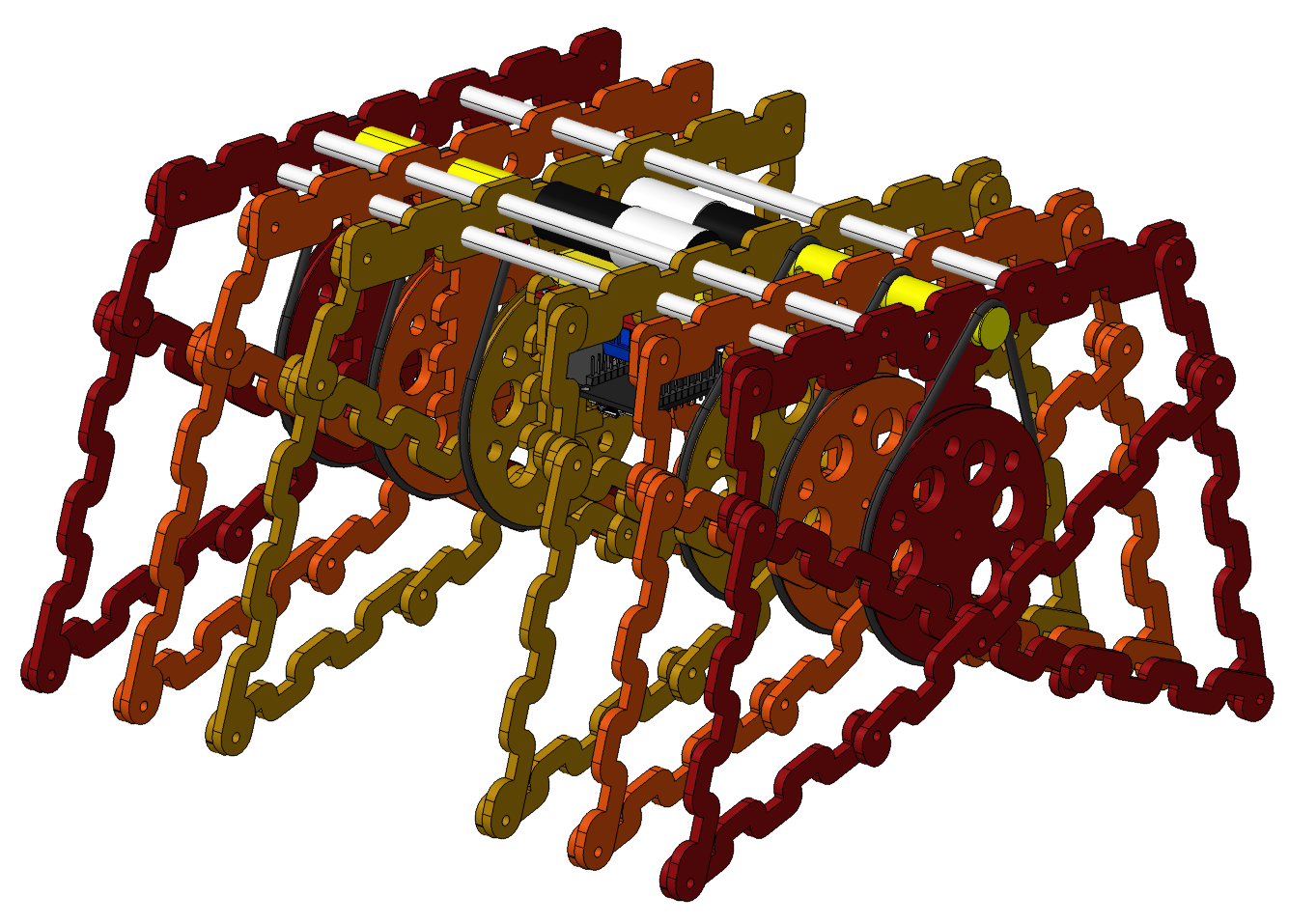
Straider linkage mechanism
Led by Wade Vagle, developed and improved the Strider and TrotBot mechanisms in 2015.
Eight-links leg mechanism.
Colombia - 2021
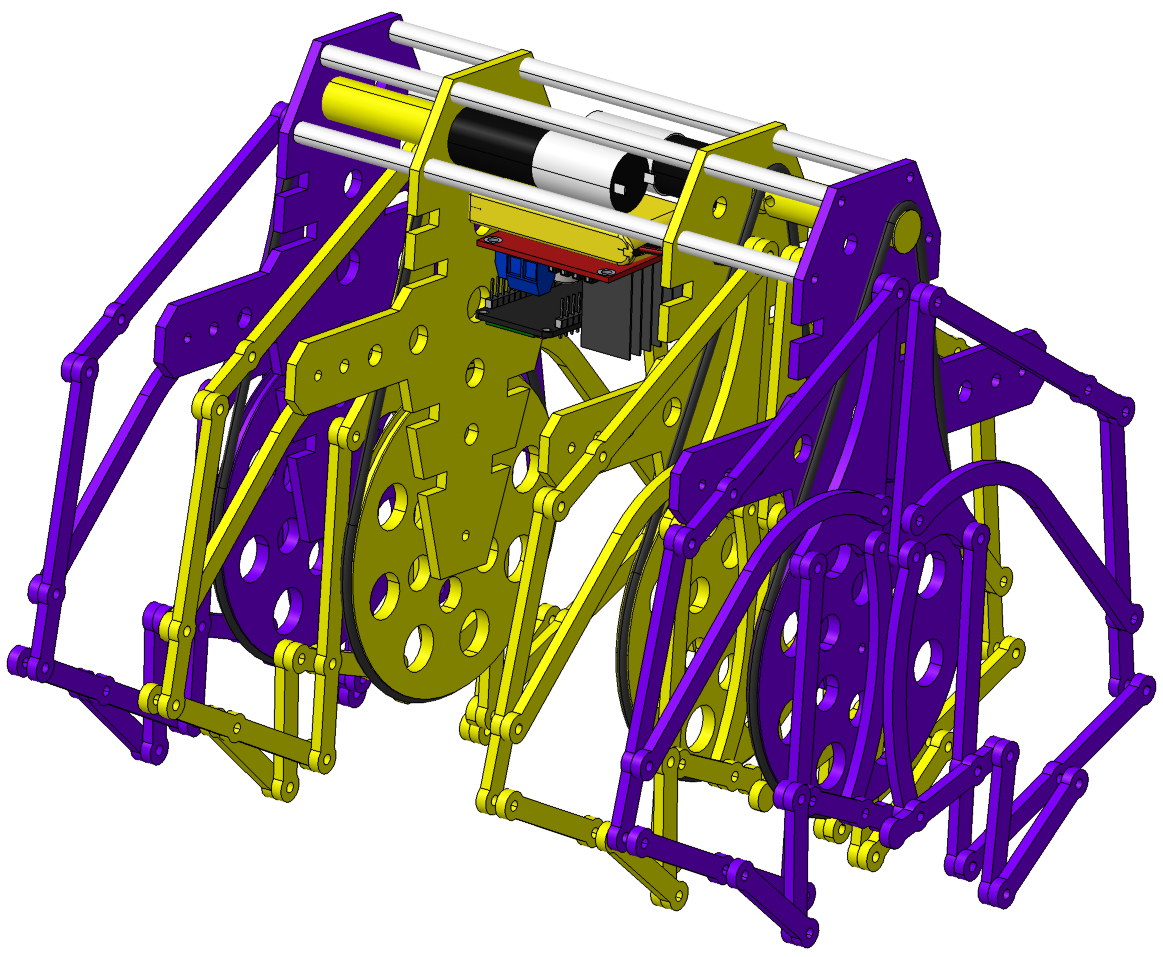
Trotbot linkage mechanism
Led by Wade Vagle, developed and improved the Strider and TrotBot mechanisms in 2015.
Eleven-links leg mechanism.
Colombia - 2021
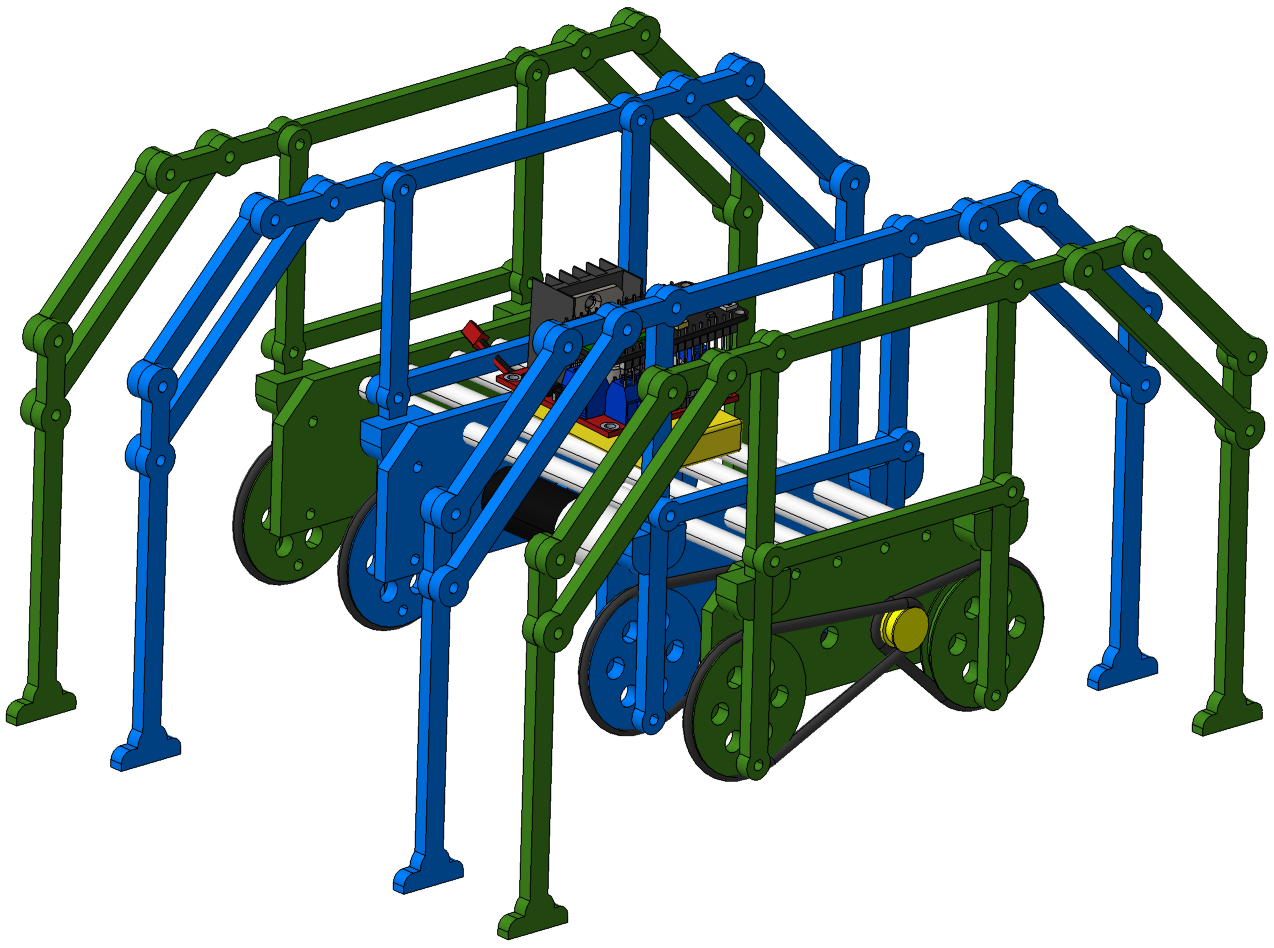
Hoecken´s linkage mechanism
Linkage mechanism that converts rotational motion to approximate straight-line motion. Invented by Karl Hoecken in 19th century.
Four-links leg mechanism.
Colombia - 2021
Stephenson´s linkage mechanism
The Stephenson has three forms depending on the link that is selected as the frame, which are denoted Stephenson I, II and III. Developed in 19th century.
Six-links leg mechanism.
Colombia - 2021
